euclid provide interfaces for both base and grid graphics that allows you to
visualise the geometries you are working with. There is only functionality
for 2D geometries so 3D geometries will be mapped to the plane given by the
mapping_plane argument. The plot method for geometries will behave like
the base plot() method and set up a new plotting window based on the
given settings. euclid_plot will add to the existing plot and thus use the
coordinate system currently in effect. euclid_grob will create a grob that
can be rendered with grid.draw().
Usage
euclid_plot(x, ..., mapping_plane = "z")
euclid_grob(
x,
...,
unit = "native",
name = NULL,
gp = gpar(),
vp = NULL,
mapping_plane = "z"
)
# S3 method for euclid_geometry
plot(
x,
y,
xlim = NULL,
ylim = NULL,
mapping_plane = "z",
add = FALSE,
axes = TRUE,
frame.plot = axes,
...
)Arguments
- x
A geometry vector
- ...
Arguments passed along to the specific drawing method.
points (and weighted points) use
points()andpointsGrob()circles use
symbols()andcircleGrob()directions and vectors use
arrows()andsegmentsGrob()iso rectangles and bounding boxes use
symbols()andrectGrob()lines, rays, and segments use
segments()andsegmentsGrob()triangles use polygon() and
polygonGrob()
- mapping_plane
either
"x","y","z", or a scalar plane geometry- unit
The unit the values in the geometry corresponds to.
- name
The name of the created grob
- gp
A gpar object giving the graphical parameters to use for rendering
- vp
A viewport or
NULL- y
ignored
- xlim, ylim
Limits of the plot scale. If not given they will be calculated from the bounding box of the input
- add
Should a new plot be created or should the rendering be added to the existing plot?
- axes
Should axes be drawn?
- frame.plot
Should a box be drawn around the plotting region?
Value
euclid_plot is called for its side effects, euclid_grob returns a
grob
Examples
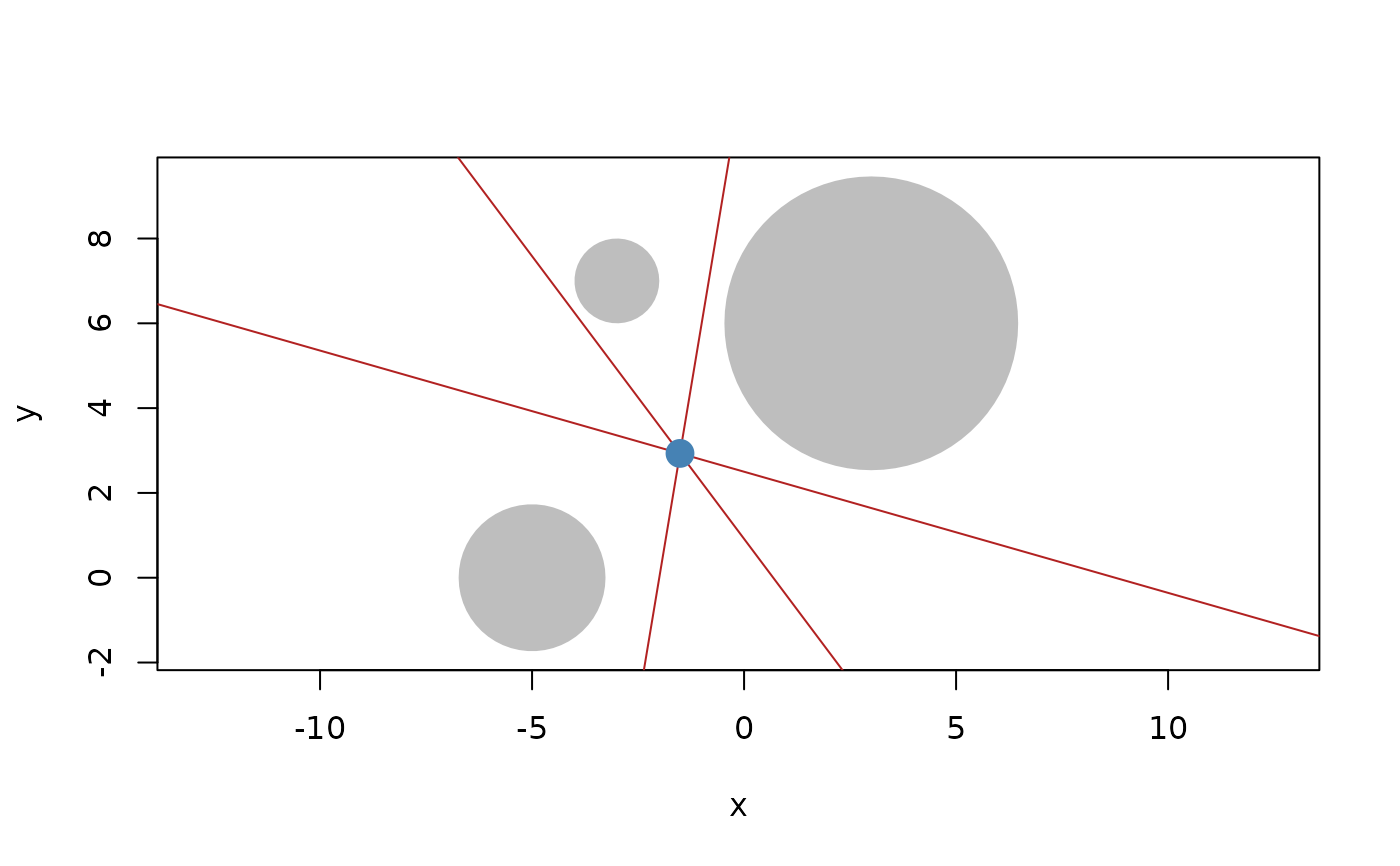
# Example visualisation of radical points and lines
c1 <- circle(point(3, 6), 12)
c2 <- circle(point(-5, 0), 3)
c3 <- circle(point(-3, 7), 1)
plot(c(c1, c2, c3), bg = "grey", fg = NA)
euclid_plot(c(
radical(c1, c2),
radical(c2, c3),
radical(c1, c3)
), col = "firebrick")
euclid_plot(radical(c1, c2, c3), pch = 16, cex = 2, col = "steelblue")